DNA-encoded Dual-Pharmacophore Glycan Library
Overview of DNA-encoded Dual-Pharmacophore Glycan Library
DNA-encoded glycan library (DEGL) is a novel technology for rapid and High-throughput Screening (HTS) of many different affinity ligand molecules. Combining DNA labeling and combinatorial chemistry, CD BioGlyco provides our clients with reassuring DEGLs such as Single-Pharmacophore Glycan Library and Trio-Pharmacophore Glycan Library. Based on a coding strategy of self-assembly of partially complementary DNA strands, our lab provides a custom DNA-encoded dual-pharmacophore glycan library. The special feature of the DNA-encoded dual-pharmacophore glycan library is the close display of two separate small molecules compared to the single-pharmacophore glycan library.
Partner With CD BioGlyco to Construct DNA-encoded Dual-Pharmacophore Glycan Library
In dual-pharmacophore glycan libraries, two distinct chemical parts are attached to the ends of complementary DNA strands that act synergistically to recognize specific molecules.
Encoded Self-assembling Chemical (ESAC) Library Technology
The DNA-encoded dual-pharmacophore glycan library consists of two sets of partially complementary oligonucleotides. Our researchers couple different molecules to the 5' and 3' ends, respectively. We use extended oligonucleotide sequences to allow them to hybridize with complementary oligonucleotides immobilized on solid surfaces.
Sublibraries are annealed through two complementary sublibraries to create large combinatorial diversity. We use Klenow polymerization to transfer code information from one sub-library to the other one. Exceptionally, flexible linkers between chemical parts and DNA facilitate glycan and glycoprotein recognition.
Workflow
During ESAC synthesis, both strands A and B bearing the two distinct chemical moieties are prepared and purified individually, offering an extremely high degree of purity to the final library. Our professional glycobiology experts provide customized services including consulting, dual pharmacophore molecule selection, synthetic route selection and optimization, library preprocessing, screening, etc. for clients.

Applications
- DNA-encoded dual-pharmacophore glycan library allows the identification of neighboring binding fragments and is widely used in fragment-based drug discovery (FBDD).
- DNA-encoded dual-pharmacophore glycan library can be used for rapid screening of glycan and glycoprotein ligands.
- DNA-encoded dual-pharmacophore glycan library can be used to develop novel glycosylation inhibitors.
- DNA-encoded dual-pharmacophore glycan library can be used for protein-protein interaction inhibitor screening.
Advantages of Us
- We provide a Klenow polymerization service that allows for the merging of coding fragment pairs into a single oligonucleotide, thus allowing for the unambiguous identification of all combinations of building blocks within a library.
- Each DNA-building block we provide can be purified separately and there is no chemical reaction between the building blocks.
- Our researchers have many years of experience in glycan library construction. Expanding the size of molecular libraries while maintaining compound activity and library purity.
Publication Data
Technology: ESAC, HTS, Copper-catalysed azide-alkyne cycloaddition (CuAAC) click, High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), DNA sequencing
Journal: Advanced Science
Published: 2020
IF: 14.3
Results: In this study, single-stranded DNA was utilized as a marker for encoding and assembly of different chemical fragments through specific sequence recognition. The diversity and complexity of the chemical libraries are increased by a modular approach that assembles the different chemical fragments into the final target molecule. Researchers use DNA-encoded chemical libraries for the isolation and characterization of small molecule ligands against multiple target proteins. This technique provides a novel and effective tool for drug discovery, especially high-throughput screening, and can significantly accelerate the discovery process of potential drug ligands.
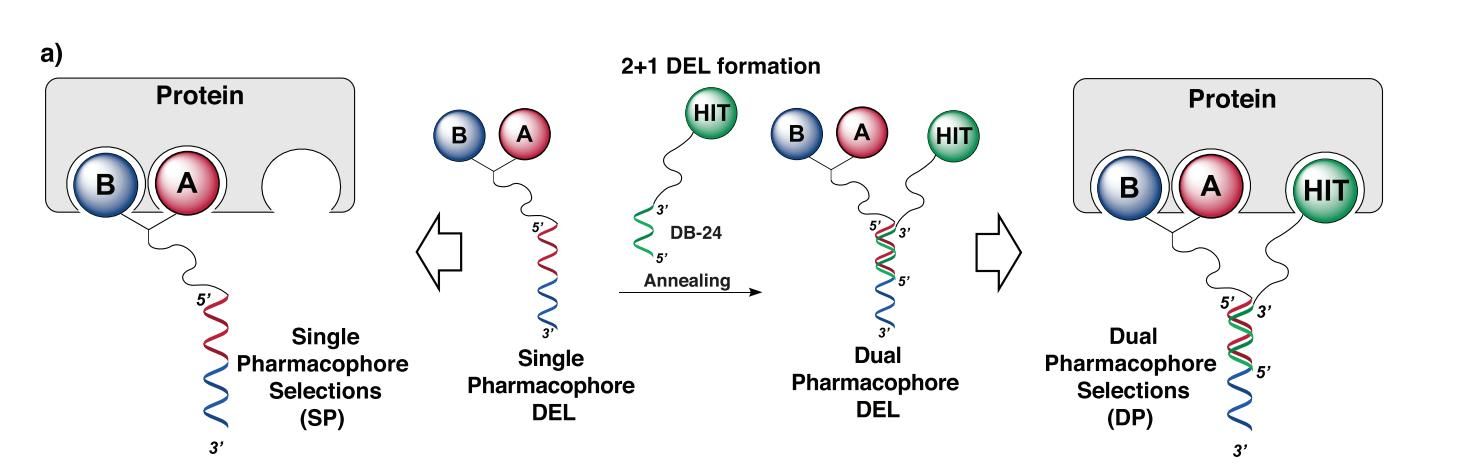 Fig.1 Schematic of single pharmacophore and in dual pharmacophore 2+1 mode. (Bassi, et al., 2020)
Fig.1 Schematic of single pharmacophore and in dual pharmacophore 2+1 mode. (Bassi, et al., 2020)
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the main principle of DEGL technology?
- The main principle of DEGL is the use of unique DNA sequence for each compound in the library. Thus, the desired compound can be screened out of a mixed library of billions of compounds and the active compound can be identified by amplification and sequencing of the DNA.
- What are the advantages of the DNA-encoded dual-pharmacophore glycan library?
- Dual-pharmacophore glycan libraries carry two chemical parts with the flexibility to reach adjacent non-overlapping binding sites of the target.
CD BioGlyco provides specialized encoding strategies for the construction of dual-pharmacophore glycan libraries. Depending on the glycan and target specificity, our glycan library construction experts provide you with the most appropriate solution. No matter what problems you encounter in DEGL development, please contact us first!
Reference
- Bassi, G.; et al.. A single-stranded DNA-encoded chemical library based on a stereoisomeric scaffold enables ligand discovery by modular assembly of building blocks. Advanced Science. 2020, 7(22): 2001970.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
Quick Links
Related Solutions


 Fig.1 Schematic of single pharmacophore and in dual pharmacophore 2+1 mode. (Bassi, et al., 2020)
Fig.1 Schematic of single pharmacophore and in dual pharmacophore 2+1 mode. (Bassi, et al., 2020)


