Magnetic Bead-based DEGL Affinity Screening
Overview of Magnetic Bead-based DEGL Affinity Screening
DNA-encoded glycan library (DEGL) screening is a highly specialized form of DNA-encoded library (DEL) screening, particularly focused on identifying glycan-protein interactions. DEGL screening leverages the principles of DEL selection to efficiently and effectively identify these interactions by accessing an immense number of glycan structures and evaluating billions to trillions of glycan-protein interactions in a single screening. Magnetic bead-based DEGL affinity screening further enhances this approach by using magnetic beads to immobilize target proteins, allowing for precise and efficient separation of bound glycans from non-binders. This method ensures specificity and accuracy, further streamlining the identification of potential therapeutic glycan-protein interactions.
The Highly Specific Selection of Glycan-Protein Interactions
Magnetic bead-based DEGL affinity screening is an advanced High-throughput Screening technique that combines the specificity of glycan-protein interactions with the efficiency of magnetic bead-based affinity selection. Magnetic beads are a crucial component in this screening method. They are typically coated with a material that can immobilize the target protein through specific interactions, such as binding to a His-tag, biotin, or other affinity tags.
Workflow

Target immobilization
The process begins with the immobilization of the target protein onto magnetic beads. The target protein is often tagged with a suitable ligand (e.g., His-tag, biotin) that binds specifically to the coating on the magnetic beads.
Incubation with DEGL
The DEGL is then introduced to the magnetic bead-bound target protein. During the incubation, glycans from the library that have an affinity for the target protein will bind to it, forming stable glycan-protein complexes.
Washing
After incubation, a series of stringent washing steps is performed. These washes are designed to remove unbound or non-specifically bound glycans, leaving only those glycans that have a true affinity for the target protein.
Elution of bound glycans
Once the washing steps are complete, the bound glycans are eluted from the magnetic beads. This is typically achieved by altering the conditions, such as changing the pH, temperature, or ionic strength, to disrupt the glycan-protein interactions.
The DNA barcodes of the eluted glycans are amplified using PCR and then sequenced using high-throughput next-generation sequencing (NGS). The sequencing data is analyzed to identify which glycans were bound to the target protein.
Hit Identification and Validation
The sequencing results reveal which glycans have the strongest affinity for the target protein. These hits are then further validated through additional biophysical and biochemical assays to confirm their binding specificity and functional relevance.
Applications
- Magnetic bead-based DEGL affinity screening is particularly valuable in identifying glycan ligands that may serve as lead compounds in drug development.
- Magnetic bead-based DEGL affinity screening aids in exploring complex glycan-protein interactions, contributing to a deeper understanding of glycoscience and its implications in health and disease.
- By consolidating large-scale screenings into a streamlined process, magnetic bead-based DEGL affinity screening reduces costs associated with reagent use, time, and labor.
Advantages
- Magnetic beads allow the highly specific selection of glycan-protein interactions, reducing the noise from non-specific bindings.
- Magnetic bead-based DEGL affinity screening allows the rapid screening of vast glycan libraries against a target protein.
- Magnetic bead-based DEGL affinity screening can handle a large number of samples simultaneously, making it suitable for high-throughput screening.
Publication
Technology: Magnetic bead-based isolation, Mass spectrometry, FLAG-tag system
Journal: Journal of biomolecular screening
IF: 2.3
Published: 2015
Results: The study successfully developed a novel magnetic bead-based ligand binding assay aimed at facilitating drug discovery for human Kynurenine 3-Monooxygenase (KMO), a key enzyme involved in several inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases. The assay addresses the significant challenges associated with the production and purification of recombinant KMO, which is complicated by a large membrane-targeting domain that affects the enzyme's stability and solubility.
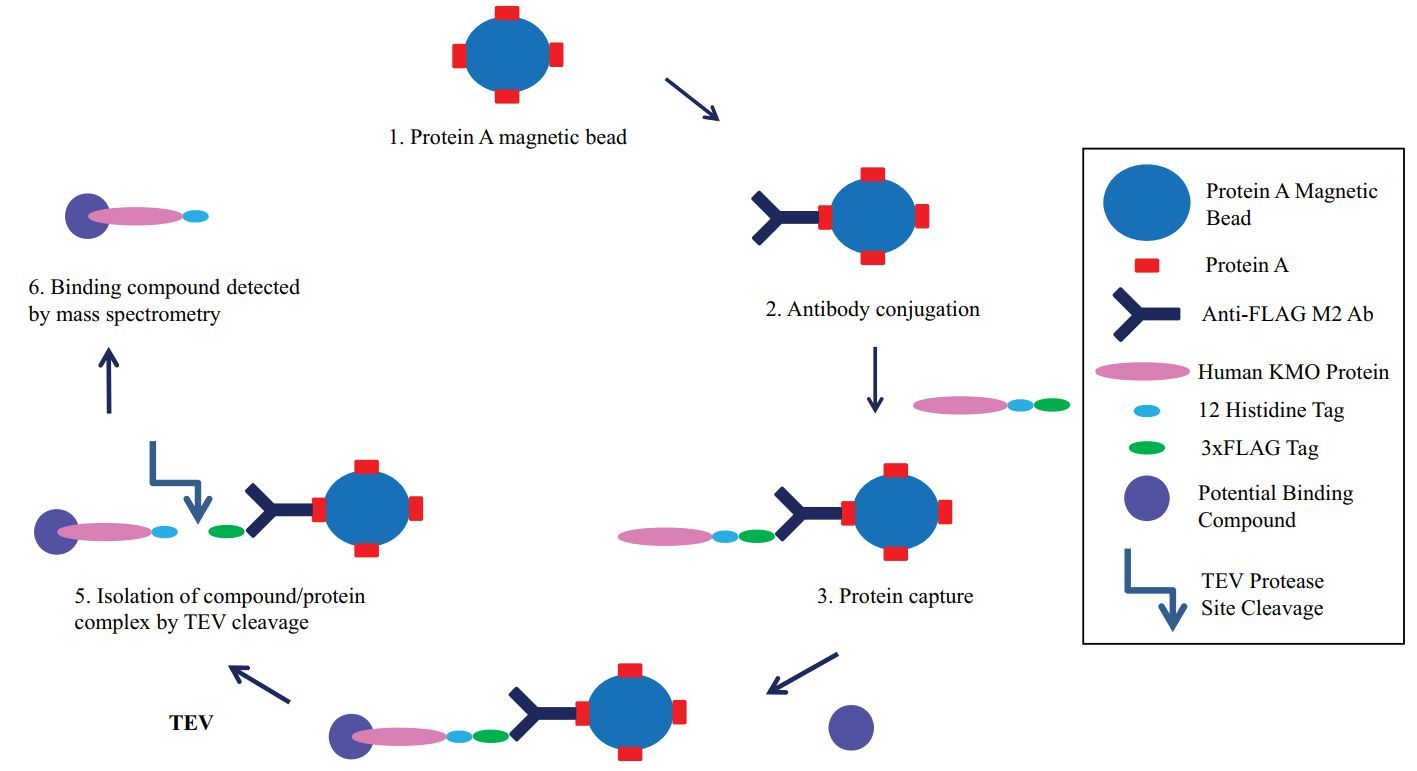 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the novel magnetic bead-based KMO drug binding assay. (Wilson, et al., 2015)
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the novel magnetic bead-based KMO drug binding assay. (Wilson, et al., 2015)
Frequently Asked Questions
- What types of proteins can be used in magnetic bead-based DEGL affinity screening?
- A wide variety of proteins, including membrane-bound, cytosolic, and extracellular proteins, can be used in this screening method. The proteins are typically tagged with ligands such as His-tag, biotin, or other affinity tags that facilitate their immobilization on magnetic beads.
- How are the results of magnetic bead-based DEGL affinity screening analyzed?
- After the screening, the DNA barcodes from the bound glycans are sequenced using next-generation sequencing (NGS). The sequencing data is then deconvoluted to identify the specific glycans that interacted with the target protein, providing insights into potential hits.
By combining the specificity of magnetic bead selection with the high-throughput capabilities of DEGL, CD BioGlyco offers a robust platform for advancing glycoscience and drug discovery. Please feel free to contact us to discover how we can support your research and development needs.
Reference
- Wilson, K.; et al. A magnetic bead-based ligand binding assay to facilitate human kynurenine 3-monooxygenase drug discovery. Journal of biomolecular screening. 2015, 20(2): 292-298.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
Quick Links
Related Solutions


 Fig.1 Schematic representation of the novel magnetic bead-based KMO drug binding assay. (Wilson, et al., 2015)
Fig.1 Schematic representation of the novel magnetic bead-based KMO drug binding assay. (Wilson, et al., 2015)


