Glycoinformatics-assisted Model Glycomics Analysis Service
Unveiling the Complexity of Model Glycomics with Precise Glycoinformatics Integration
Glycomics is a class of science that explores, describes, and researches the structure of all carbohydrates produced by a given system, and this can be done at the level of whole organisms or individual cell or tissue types. Selected organisms, cells, or tissues in nature provide the glycobiology community with a wealth of information on glycan function. Glycomics analysis at the level of certain organisms or cell models is an important tool for researching glycan epitopes.
At CD BioGlyco, we have gained proficiency in glycoinformatics-related knowledge to provide our clients with a wide range of Glycoinformatics Services. On this basis, we combine glycoinformatics techniques with glycobiological methods to provide reliable model glycomics analysis services to our clients.

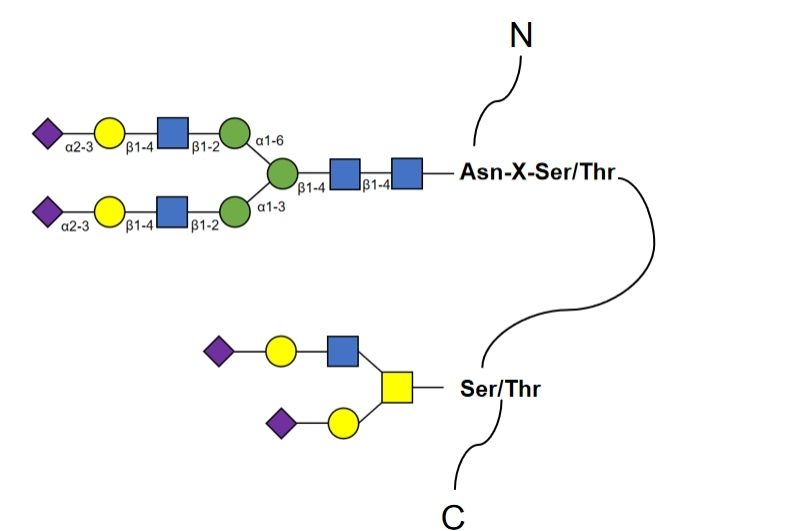
Glycan sequencing
After we incubate the cell samples with lectin, we amplify the released nucleotides using primers containing cellular oligonucleotide sequences, purify the amplified products by gel electrophoresis, and sequence them using a sequencer. On this basis, we match the obtained glycan structure with the existing carbohydrate structure database, which can rapidly characterize the glycan. In addition, glycan sequencing technology can be directly used to analyze micro glycans in both juvenile and adult mammals.
Structural analysis of glycans
According to data from the carbohydrate structure database, mannose and glucose are the most common monomer structures in fungal glycans, along with acetate residues, which may be derived from 2-acetamido-2-deoxy-glucopyranose residues. Whereas in bacterial glycans, acetate is the most common residue. Other common bacterial monomers include α- and β-d-galactose, α- and β- d -glucose, and so on.
Here we offer a wide range of mass spectrometry (MS) and chromatography techniques to analyze glycans, monomers, and glycoconjugates from animals, fungi, or bacteria.
Matching the monomeric structure of a glycan to a structure in a database allows rapid tracing of the origin of the glycan. When used in conjunction with fluorescent labeling, the metabolic pathway of the glycan can also be traced.
In addition, MS-based glycan analysis techniques are capable of obtaining glycan chain profiles in vivo in models and can characterize glycan chain abundance.
For example, analysis of glycocomplexes in the zebrafish organism using MS-based techniques revealed a diversity of glycoconjugates. Glycan profiles of major glycoproteins and glycolipids in fertilized eggs and early embryos of zebrafish showed a diversity of glycan structures in the zebrafish embryo, with two types of glycans, salivating glycan chains and high mannose-type glycan N-glycan chains, expressed in high abundance at all stages of embryonic development.
Glycan distribution
The distribution of glycosidic bonds in the glycans of model organisms can be obtained using the statistical tools of the carbohydrate structure database. These data allow estimation of the pool of glycosyltransferases required to cover the glycanome of a particular taxon, and also assessment of the monosaccharide building blocks required for automated synthesis of the glycans of a particular taxon.
Here, the specific models contained in the glycoinformatics-assisted model glycomics analysis service we provide include but are not limited to, the following.
- Mice
- Frog
- Bacteria
- Silkworm
- Sea Anemone
- Rat
- Drosophila Melanogaster
- Fungi
- Rabbit
- Leech
- Zebrafish
- Human Tissue
- Caenorhabditis Elegans
- Dog
- Marine Worm
Publication Data
Technology: Glycan-seq
Journal: ISME Communications
IF: 4.3
Published: 2022
Results: In this research, the authors utilized a highly multiplexed glycan analysis method, Glycan-seq, for glycan analysis of mouse intestinal bacteria. The evaluation of cultured radiation-resistant Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and Escherichia coli showed significant differences in glycan profiles between these bacteria, which were screened by the authors and analyzed in depth by flow cytometry. Comparing the results of the experiments, the authors found that the results of the flow cytometry analyses were the same as those of Glycan-seq, which also demonstrated that Glycan-seq can be used for bacterial glycan analysis. Next. The authors used Glycan-seq to analyze the glycans of the intestinal flora of puppies and adult dogs and found that the glycan profiles of the intestinal flora of puppies and adult dogs were significantly different, which demonstrated the different bacterial compositions of the intestinal flora of puppies and adult dogs.
 Fig.1 Experimental workflow of the Glycan-seq. (Oinam, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Experimental workflow of the Glycan-seq. (Oinam, et al., 2022)
Applications
- By using glycoinformatics tools, large-scale glycomics data from mods can be analyzed and interpreted, including the composition, structure, and function of glycans. This helps researchers understand the complexity and diversity of glycans or glycoconjugates in various organisms.
- Glycans play an important role in the development and progression of many diseases. Analyzing the glycomes of models, can provide clues for early diagnosis of diseases and guide personalized treatment.
- Glycans play important roles in interactions and signaling in organisms. By analyzing the glycomics groups in different models, the drug development process can be accelerated and safer and more effective drugs can be discovered.
Advantages
- Our model glycomics analysis service team consists of a group of scientists and researchers with extensive experience and expertise in the fields of glycobiology, bioinformatics, and molecular biology.
- Our team provides comprehensive services, from data acquisition and analysis to result interpretation and report writing, to provide one-stop Glycomics Analysis Solutions for our clients.
- We adopt stringent data protection measures to ensure the security and confidentiality of our client's data, allowing them to entrust their research and analysis tasks with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Why glycoinformatics-assisted modeling is needed for glycomics analysis?
- Glycoinformatics provides a systematic approach to analyzing the structure and function of glycan molecules, which can effectively help to solve complex metabolomics problems of glycans. Combined with modeling analysis, it can more accurately understand the mechanism and potential impact of glycan molecules in the immune system, help researchers discover the key information hidden behind the structure of glycan molecules, and provide important support for research on immune-related diseases, drug discovery and development, and so on.
- What are the value and application areas of the glycoinformatics-assisted model glycomics analysis service?
- This service can be used in a variety of immune-related disease research, drug development, and biomedical fields to help reveal the important role and potential mechanisms of glycan molecules in the immune process. In addition, personalized medicine and precision medicine can be supported by such services, which can help identify potential immunotherapy targets and conduct research on the diagnosis and treatment of related diseases.
CD BioGlyco utilizes the latest bioinformatics technology combined with glycobiology tools to provide high-quality model glycomics analysis services to our clients. Our team offers glycomics analysis services covering a wide range of animal models for research needs in several fields. Please feel free to contact us if you still have questions about this and we will be happy to answer them.
Reference
- Oinam, L.; et al. Glycan profiling of the gut microbiota by Glycan-seq. ISME Communications. 2022, 2: 1.
For research use only. Not intended for any diagnostic use.
Quick Links
Related Services



 Fig.1 Experimental workflow of the Glycan-seq. (Oinam, et al., 2022)
Fig.1 Experimental workflow of the Glycan-seq. (Oinam, et al., 2022)