


100 N-glycan microarray service of CD BioGlyco helps researchers investigate the binding properties of proteins, antibodies, cell cultures, bacteria or other potential biological samples to an array of 100 basic N-glycans. The glycan microarray platform established by our company ensures that we provide customers with high-quality scientific services to accelerate their research.
N-linked protein glycosylation is a commonly occurring co-translational and post-translational modification and it is estimated that the majority of all secreted proteins are N-glycosylated. N-glycosylation modifications play an important role in the proper folding, functional localization, and intracellular transport of proteins. In mammals, N-glycosylation is important for the regulation of embryonic development, cancer development, and immune defense. In plants, N-glycosylation is significant for many physiological processes such as cell wall formation, reproductive development and defense against pathogenic bacteria invasion.
Complex N-glycans are involved in a wide range of cellular processes in mammals, especially in intercellular interactions and immune cell functions, so they are generally considered by researchers as the preferred glycan candidates for the investigation of carbohydrate-binding-vaccines like HIV broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAb). The basic N-glycan structures offered in our 100 N-glycan microarray could help researchers understand the binding determinants underlying antibodies or other proteins of interest.
Our service for 100 N-glycan microarrays employs fundamental advanced technologies ensuring exceptional reliability and analytical performance. Central to this platform, a curated collection of one hundred chemically identified N-glycans spans wide structural heterogeneity—incorporating high-mannose configurations, hybrid architectures, and complex-type glycoforms. Multiple structures demonstrate biological significance. These glycans undergo exact deposition upon functionalized glass slides, yielding microarrays of high density. Array stability and reproducible functioning derive from printing and immobilization through proprietary methods. This permits consistent, sensitive measurement of interactions between glycans and proteins—critical for elucidating diverse biological processes.
CD BioGlyco provides customers with microarray service for 100 N-glycans, including 81 complex and hybrid N-glycans, 10 high-mannose N-glycans and 9 Neu5Gc-N-glycans. The service we provide include but are not limited to:
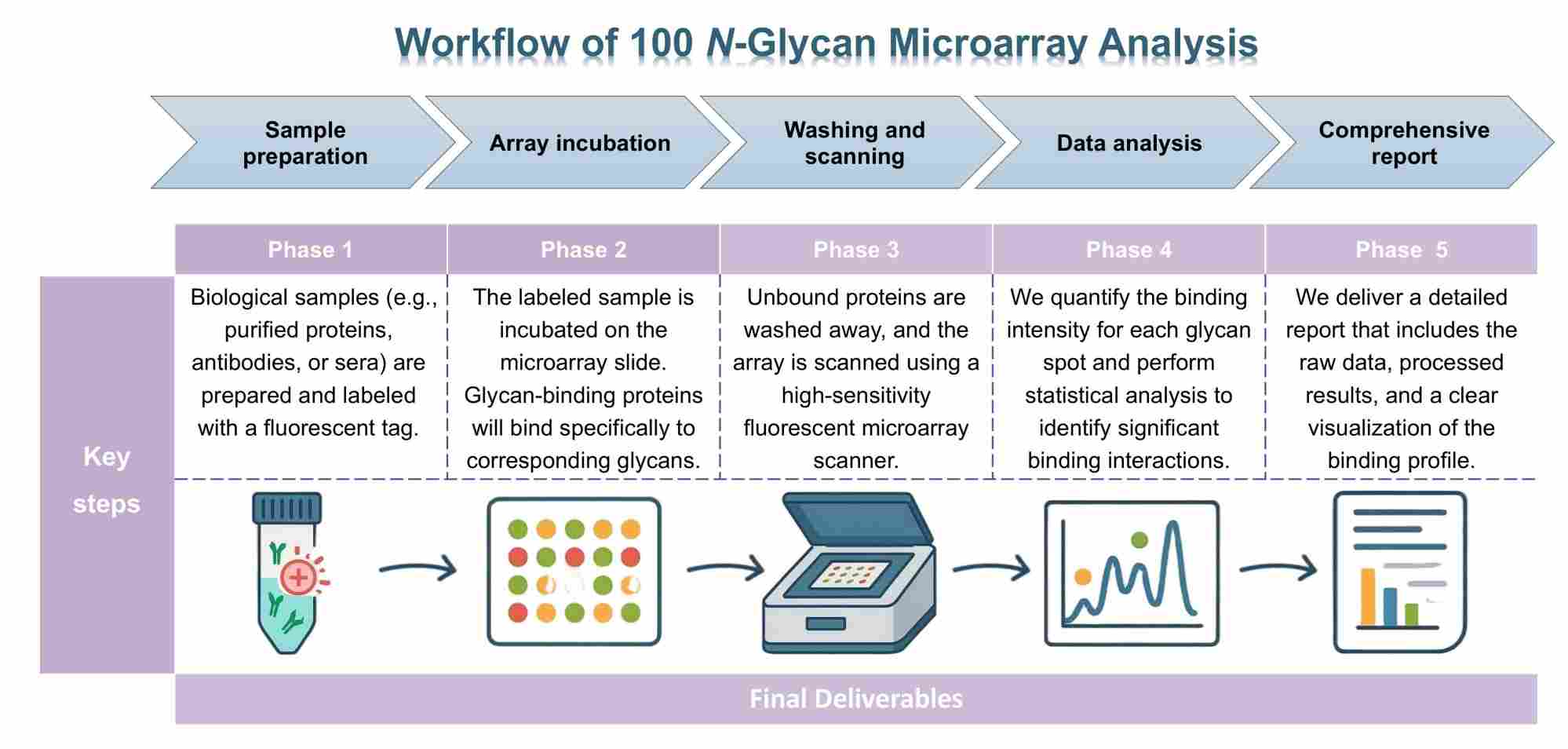
Your biological samples (e.g., purified proteins, antibodies, or sera) are prepared and labeled with a fluorescent tag. This step is critical to ensure accurate detection of binding events.
The labeled sample is incubated on the 100 N-glycan microarray slide. During this step, any glycan-binding proteins in your sample will bind specifically to their corresponding glycans on the array.
Unbound proteins are washed away, and the array is scanned using a high-sensitivity fluorescent microarray scanner. This captures the binding signal, generating a raw data image.
The raw image data is then processed using specialized software. We quantify the binding intensity for each glycan spot, normalize the data, and perform statistical analysis to identify significant binding interactions.
We deliver a detailed report that includes the raw data, processed results, and a clear visualization of the binding profile. Our experts are available to help you interpret the findings and discuss their biological implications.
DOI.: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00833
Journal: Frontiers in Chemistry
Published: 2019
IF: 4.2
Results: This review details the development and immunological applications of glycan microarrays as essential tools for identifying glycan recognition by immune proteins. The authors describe the chemical strategies for constructing these microarrays, particularly covalent attachment methods using bifunctional linkers like AEAB and F-MAPA to immobilize diverse glycans while preserving structural integrity. They highlight how glycan microarrays enable high-throughput profiling of glycan-binding proteins (GBPs) such as siglecs and galectins, revealing their specificities for sialylated or LacNAc-containing glycans. The review emphasizes the role of these arrays in immunological discoveries, including identifying natural ligands for endogenous immune receptors, characterizing pathogen-host interactions (e.g., influenza, rotavirus), and mapping the human anti-glycan antibody repertoire. Innovations like DNA-coded arrays, Luminex bead arrays, and cell-based platforms are also discussed as emerging methods to enhance throughput and biological relevance. Overall, glycan microarrays are portrayed as indispensable for deciphering glycan-mediated immune mechanisms and advancing diagnostic and therapeutic research.
Our 100 N-glycan microarray decodes functional glycan signatures across biological systems—revealing critical targets in cancer, infection, and immune regulation. To transform these insights into precision interventions, we offer N-Glycosylation Inhibitor Development Services that disrupt glycan biosynthesis or interactions through complementary strategies.
CD BioGlyco offers a range of glycan microarray analysis services. These help our customers speed up their scientific research and obtain reliable data by using our microarray platform to perform highly parallel glycan expression level analysis. If you need our services, please contact us for further consultation.
Reference:
