


Only endothelial cells express the glycoprotein known as E-Selectin (CD62E). It was initially identified as a leukocyte adhesion molecule on activated endothelial cells by Bevilacqua and associates in the 1980s. Skin and bone marrow microvessels produce E-Selectin on a constitutive basis, but endothelial cells in other tissues do not, although their expression is significantly increased by inflammatory cytokines like TNF- and IL-1. Although not fully understood, the release of a soluble version of E-Selectin and the internalization of the molecule have been proposed as explanations for this fast upregulation. The control of leukocyte accumulation in inflammatory reactions may depend on this modulation of E-Selectin expression.
E-Selectin has a typical molecular weight of 64 kD, although various glycosylated variants have been found to have relative molecular weights of 100 and 115 kDa. An amino-terminal lectin-like domain, an epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domain, and six repeating motifs like those in certain complement-binding proteins make up the core structure of E-Selectin. While the function of the complement binding-like sections is not yet clear, they likely work, at least in part, as spacers to keep the other domains away from the cell surface. The lectin-like domain and EGF-like domain mediate contact with leukocytes.
Numerous structures carried by glycoproteins are recognized by E-Selectin. Based on that, CD BioGlyco provides Custom Glycoprotein Synthesis including Chemoenzymatic Synthesis and Chemical Synthesis for customers to help them produce custom glycoproteins.
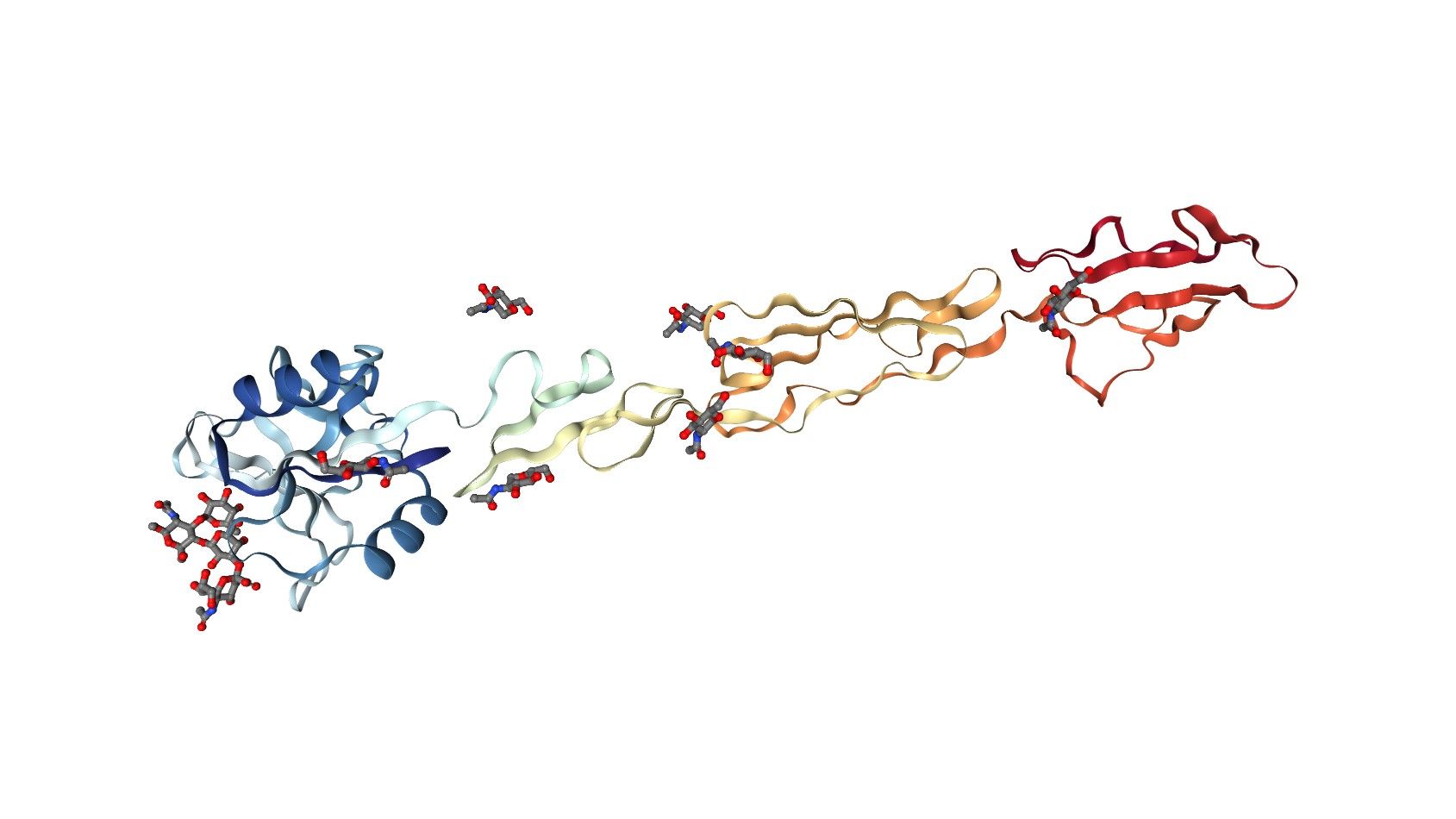 Fig.1 E-Selectin, EGF-like, and two SCR domains complexed with Sialyl Lewis X. (PDB)
Fig.1 E-Selectin, EGF-like, and two SCR domains complexed with Sialyl Lewis X. (PDB)
The expression of E-Selectin on endothelium is associated with acute or chronic inflammatory responses because E-Selectin interacts with ligands on the surface of immune cells to facilitate the recruitment of immune cells. And E-Selectin has a detrimental role not just in inflammatory diseases but has also been found in several cancer tissues, suggesting a possible role in the development of this illness. Adhesion of tumor cells on the vascular endothelium of the target organ is a key step in the cascade of metastasis. The pair SLEx/E-Selectin is now well established as a key mediator in the adherence of cancer cells to the endothelium during the development of metastases through a process akin to immune cell adhesion. Leukocyte transmigration has been demonstrated to be inhibited by monoclonal antibodies (MABs) directed against E-Selectin. According to some theories, when leukocytes attach to E-Selectin on active endothelium, CD11b (Mac-1) on the leukocytes is upregulated, leading to an increase in adhesion through the interaction of ICAM-1/Mac-1.
E-Selectin has evolved into a natural target for therapeutic intervention as a result of this demonstrated expression of E-Selectin in the vicinity of inflammation, infection, or malignancy. The use of E-Selectin as a receptor for the administration of anti-inflammatory or anti-cancer medications as well as for medical imaging systems comprising an imaging agent is a significant tactic.
 Fig.2 Schematic representation of the different concepts used to target E-Selectin. (Jubeli, et al., 2012)
Fig.2 Schematic representation of the different concepts used to target E-Selectin. (Jubeli, et al., 2012)
CD BioGlyco has an advanced Microarray Platform for customers to explore the functions of E-Selectins. We have confidence to meet customers’ requirements about sciences research, if you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us for more information.
References
