


Prototype galectins have one carbohydrate recognition domain (CRD). Each Galectin has a separate carbohydrate binding preference. Many Galectins are bivalent or multivalent in terms of their carbohydrate-binding activity, and some mono-CRD Galectins exist as dimers.
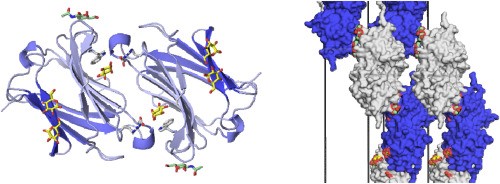
 Fig.1 Prototype Galectins and mode of self-association. (Ayona, et al., 2020)
Fig.1 Prototype Galectins and mode of self-association. (Ayona, et al., 2020)
The family members of prototypal Galectins are Gal-1, -2, -5, -7, -10, -11, -13, -14, -15, and -16, they all have one CRD. They have different properties in process of biology.
 Galectin-1
Galectin-1
Galectin-1 is a protein that is encoded by the LGALS1 gene. Galectin-1, which may form homodimers, has a crystal structure that is made up of six and five-stranded sheets arranged in an antiparallel pattern. The unusual secretion of Galectin-1 has recently been demonstrated to depend on cell-surface glycans that have an affinity for the protein. It contributes to the establishment of the synapse between pre-B cells and stromal cells in the immune system by binding to the pre-B cell receptor (BCR). This interaction facilitates pre-BCR activation. Galectin-1 controls cytokine synthesis, proliferation, and apoptosis, which can have an impact on T-cell homeostasis. Through processes unrelated to its capacity to trigger apoptosis, Galectin-1 also has an impact on the physiology of monocytes, macrophages, and other antigen-presenting cells.
 Galectin-2
Galectin-2
The LGALS2 gene in humans encodes the protein Galectin-2. Galectin-2's X-ray crystallography reveals that it is complexed with lactose and that it forms as two-fold symmetric dimers with two extended antiparallel -sheets arranged in a -sandwich. T-cell apoptosis can be induced by Galectin-2. In a mouse model of colitis, the amount of Galectin-2 expression is negatively correlated with the severity of the condition. Recombinant Galectin-2 therapy of mice resulted in mucosal T-cell death and decreased colitis in this model.
 Galectin-5
Galectin-5
Galectin-5 is a rat lectin, and its binding to glycans is modulated by sialylation and N-glycan core substitutions. it has a high affinity for polyvalent glycans with unmasked N-acetyllactosamine and for terminal histo-blood group AB extensions. Galectin-5 has an exceptionally low propensity for dimer formation in the absence of multivalent ligands and its strict cell-type–specific expression pattern.
 Galectin-7
Galectin-7
Galectin-7 is a homodimeric prototype Galectin with one CRD. It is mainly present in the epidermis and can induce apoptosis of stimulated T-cells in a manner dependent upon caspase-1, -3, and -8, but not caspase-9. Overexpression of Galectin-7 in mice compromises the skin by leading to loss of cell junctions and defective skin repair.
 Galectin-10
Galectin-10
A prototype Galectin called Galectin-10 exists as dimers. it is also known as Charcot-Leyden crystal protein because it has been found to crystallize when eosinophils are drawn to an inflammatory area. Eosinophils and basophils both contain substantial levels of Galectin-10, which is also produced by CD4+/CD25+ regulatory T-cells, that are crucial for the downregulation of antiself responses. Since Galectin-10 hasn't been identified in any other animals, it may be a human-specific Galectin. Galectin-10 can cause inflammation in bronchitis and acute peritonitis. Additionally, a recent study found that primary human macrophage absorption of Galectin-10 induces the release of IL-1.
 Galectin-11
Galectin-11
Galectin-11 is a novel host mediator targeting specific stages of the gastrointestinal nematode parasite. It is released from epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract, specifically the following infection with gastrointestinal parasites including the highly pathogenic nematode. The function of Galectin-11 is currently unknown but seems to be associated with the development of immunity by the host.
 Galectin-13
Galectin-13
Galectin 13 (Gal-13), also known as LGALS13 and placental protein 13 (PP13), is the most studied Galectin of anthropoid primates. It shows structural and functional homologies to the ß-galactoside-binding lectins, with high homology to the other members of the cluster in their CRD. Galectin-13 has a high affinity to sugar residues, especially to N-acetyl glucose amine, fucose, and N-acetyl galactose amine. It also binds sugar residues of the B and AB antigens of the ABO blood groups, a binding that regulates the availability of free Gal-13 in the blood of pregnant women.
 Galectin-14
Galectin-14
Prototype Galectin-14 (Gal-14) is more expressed in the human placenta than any other Galectin, which suggests that it may be involved in fetal development and immunological tolerance control during pregnancy. The dimeric Galectin Gal-14's crystal structure reveals that its overall fold differs greatly from other Galectins due to the presence of two -strands (S5 and S6) that stretch from one monomer and contribute to the other's carbohydrate-binding domain. Even while lactose was unable to stop Gal-14 from inducing agglutination in chicken erythrocytes, the hemagglutination assay demonstrated that this lectin could. Gal-14 differs from Galectin-1, Galectin-3, and Galectin-8 in that it includes two essential amino acids—a histidine and an arginine—in the ordinarily conserved, canonical sugar-binding region instead of glutamine (Gln53) and arginine (His57).
 Galectin-15
Galectin-15
In sheep, Galectin-15 (LGALS15) is expressed specifically in the endometrial luminal (LE) and superficial glandular (sGE) epithelia of the uterus in concert with blastocyst elongation during the peri-implantation period. The temporal and spatial alterations in LGALS15 mRNA and protein in the uterine endometrial LE and sGE and lumen during the peri-implantation period of early pregnancy in sheep, combined with known biological activities of other Galectins, make LGALS15 a strong candidate mediator of conceptus-endometrial interactions during implantation.
 Galectin-16
Galectin-16
No studies are available on native Galectin-16 at the protein level, only recombinant protein has been tested. Recombinant Galectin-16 is a monomeric protein, which is composed of 142 amino acids and has a typical Galectin structure of the CRD β-sandwich with two sheets formed by six β-strands on the concave side (S1–S6) and five β-strands on the convex side (F1–F5). Galectin-16 lacks lactose-binding ability unless arginine (Arg55) is replaced with asparagine in the S4 β-strand. LGALS16 with two other Galectins (LGALS13 and LGALS14) were found to be upregulated in differentiated trophoblast cells to confer immunotolerance at the maternal-fetal interface. LGALS16 is detected in diverse human cells/tissues and alters expression in association with cancer, diabetes, and brain diseases.
CD BioGlyco has advanced glycoengineering platform and carbohydrate-based glycomedicine development platform for customers to study prototype Galectins and provides customized services according to research needs. if you are interested in our services, please feel free to contact us for more detailed information.
Reference
